Acne types
What type of acne do you have?
Acne is disease that comes in many different forms. The first step should be identifying what type of acne you have, to receive the best treatment for you. To get an accurate diagnosis of your acne you should visit a professional GIGI cosmetician
Blackheads
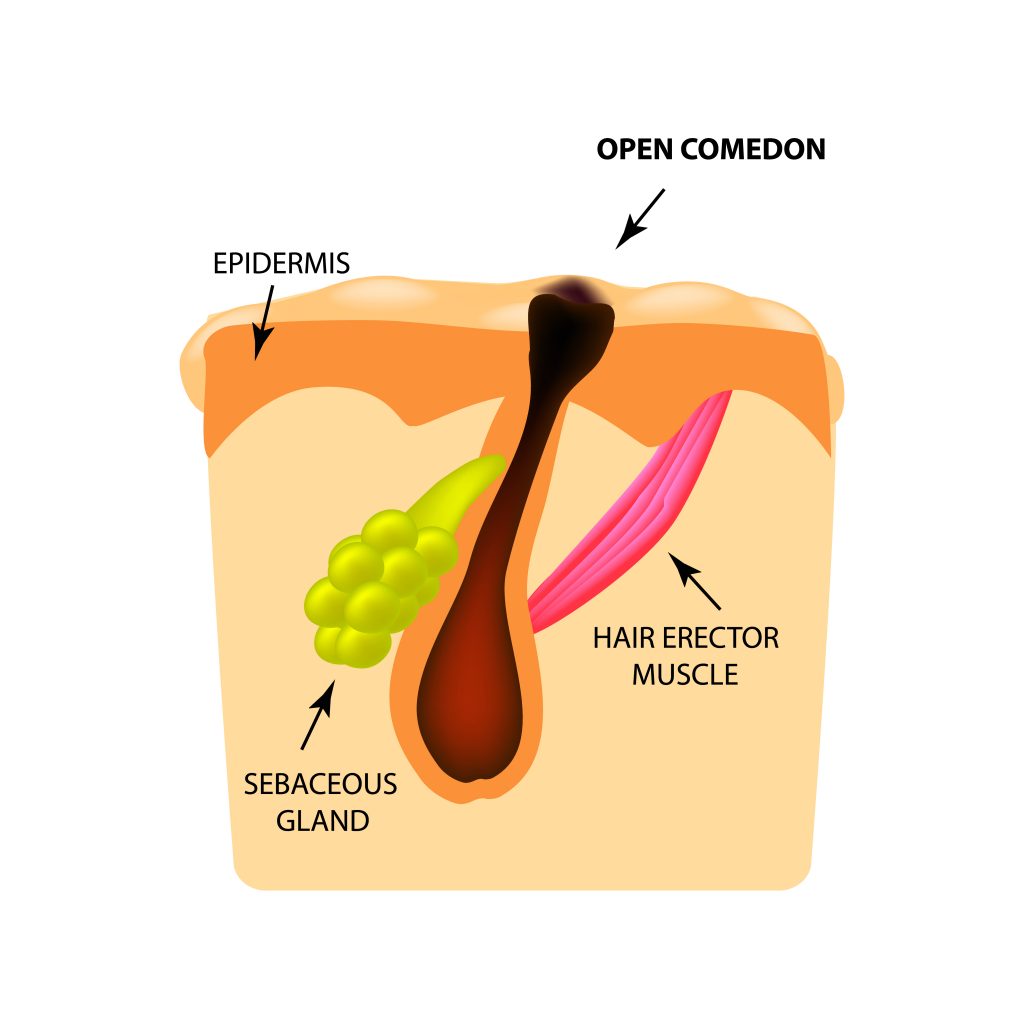
What is the cause for blackheads?
As was described in “Causes for acne-prone skin”, an acne spot begins with excess sebum production that clogs pores due to adhesion of dead skin cells and P. acnes bacteria growth inside the hair follicle. If immune system is not activated by the clogged pore, and there is no infection, redness of swelling of the pore, the clogged pore is referred to as a comedone. Comedones are an uninflammatory form of acne
Comedone is a clogged hair follicle/pore. If the pore is exposed to air, the dead skin cells that contain melanin are oxidized and become dark grey or black, hence the name-blackheads. Just like if you would take a bite off an apple and leave it on the kitchen counter, the exposed part would become dark due to oxidation. Ironically, the spot can remain white if the skin pigment (melanin) is not exposed to air. The dark color of the clogged pore is not caused by dirt or left-over makeup, therefor, you cannot wash it out.
Blackheads are one of the first signs of puberty, cause by excess sebum secretion due to elevated hormone levels. Adults with oily skin would also have many blackheads especially in the T-zone area of the face (forehead, nose and chin).
Although blackheads are usually located in the T-zone area, they can appear in other areas as well, such as back, chest, arms and anywhere there is a high density of hair follicle attached to a sebaceous gland.
Using comedogenic oils or water proof makeup can cause blackheads. Products that do not clog pores and do not cause comedones are called non-comedogenic, look for this label on products you wish to purchase, keeping your pores clean.
Whiteheads
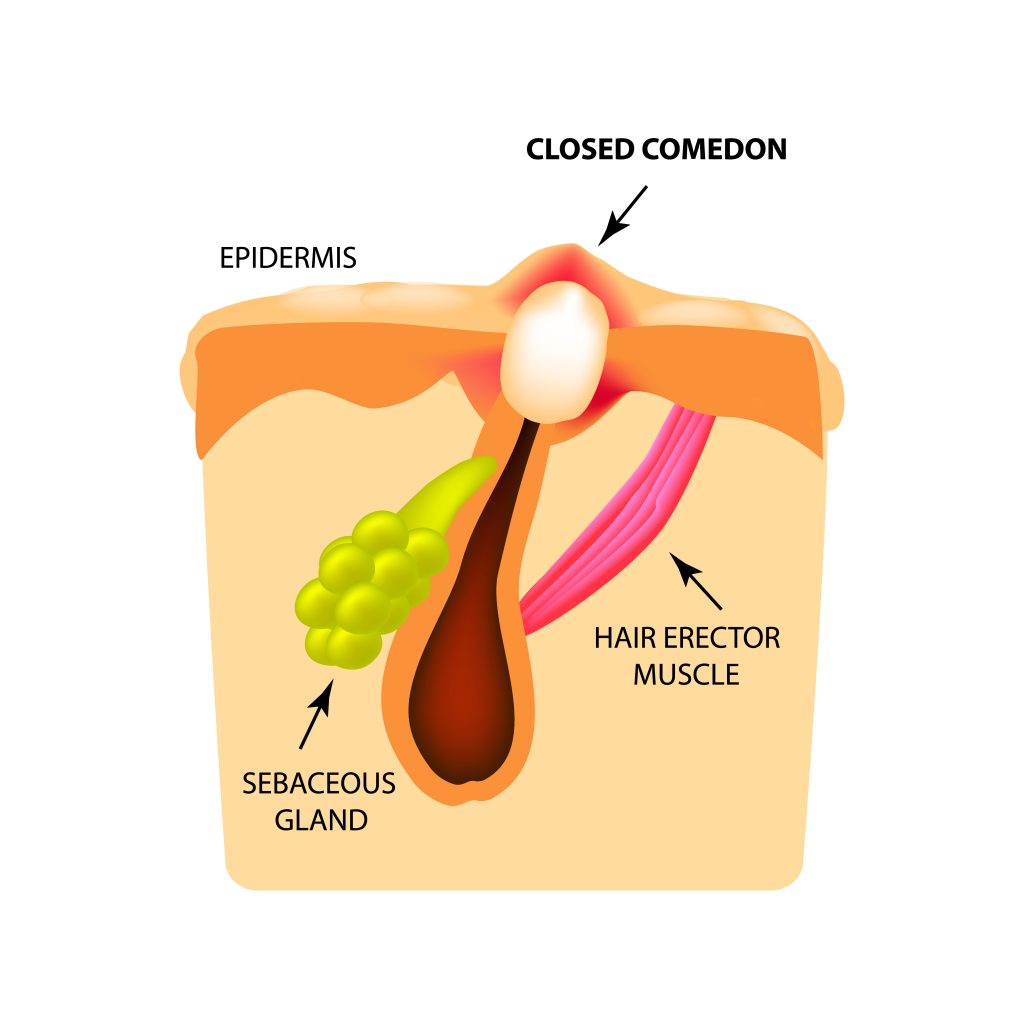
Whiteheads are a form of uninflammatory acne without any redness or puffiness of the spot. Whiteheads begin same as other types of acne: excess sebum secretion which causes adhesion of dead skin cells and form a comedone. Basically, whitehead is a clogged pore covered by a thin layer of skin.
Since the sebum and dead skin cells inside the comedone are not exposed to air, it remains white or yellow, the color of natural sebum. As opposed to blackheads, which are comedones exposed to air (not covered by skin), the color of the sebum and the dead skin cells turns to black due to melanin oxidation. Moreover, same as blackheads, whiteheads appear not only on the face, they can appear on the back and other body parts as well.
Certain cosmetic products, including moisturizers, makeup and sunscreens and even some cosmetic procedures such as wax for hair removal, can clog pores. Try to look for products labeled “non-comedogenic”, these products hopefully will not clog your pores and help avoid black/ whiteheads. Cleaning the comedones out yourself can lead to an infection of the pore and the development of an infected spot, so make sure you use a professional cosmetician to clear out your skin.
Inflammatory Acne
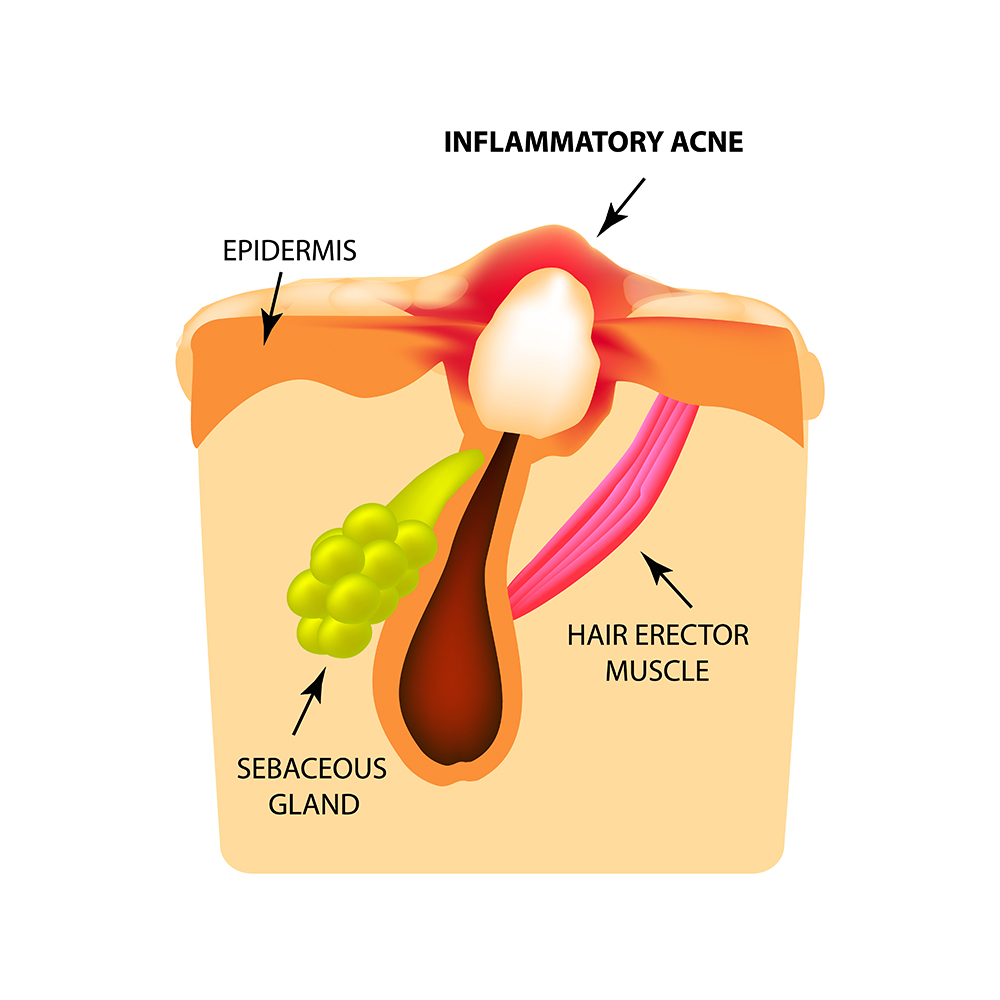
What is inflammatory acne? and how it is formed?
When our pores get clogged by sebum, dead skin cells and P. acnes bacteria, the immune system reacts by sending white blood cell to the area to fight the infection. The infected pore area increases and becomes red and swollen. This type of acne is referred to as inflammatory acne.
Inflammatory acne is a result of a tear in the hair follicle which causes a leak from the pore of sebum, dead skin cells and P. acnes bacteria into the skin. The skin protects itself by sending white blood cells to the area and creating pus. If the tare is near the skin surface the spot will be small and heal quickly. As the tare develops deeper in the skin tissues, the risk of developing a substantial cyst or pustule increase. Large inflamed spots are painful and red due to high supply of blood to the area.
Types of inflammatory acne
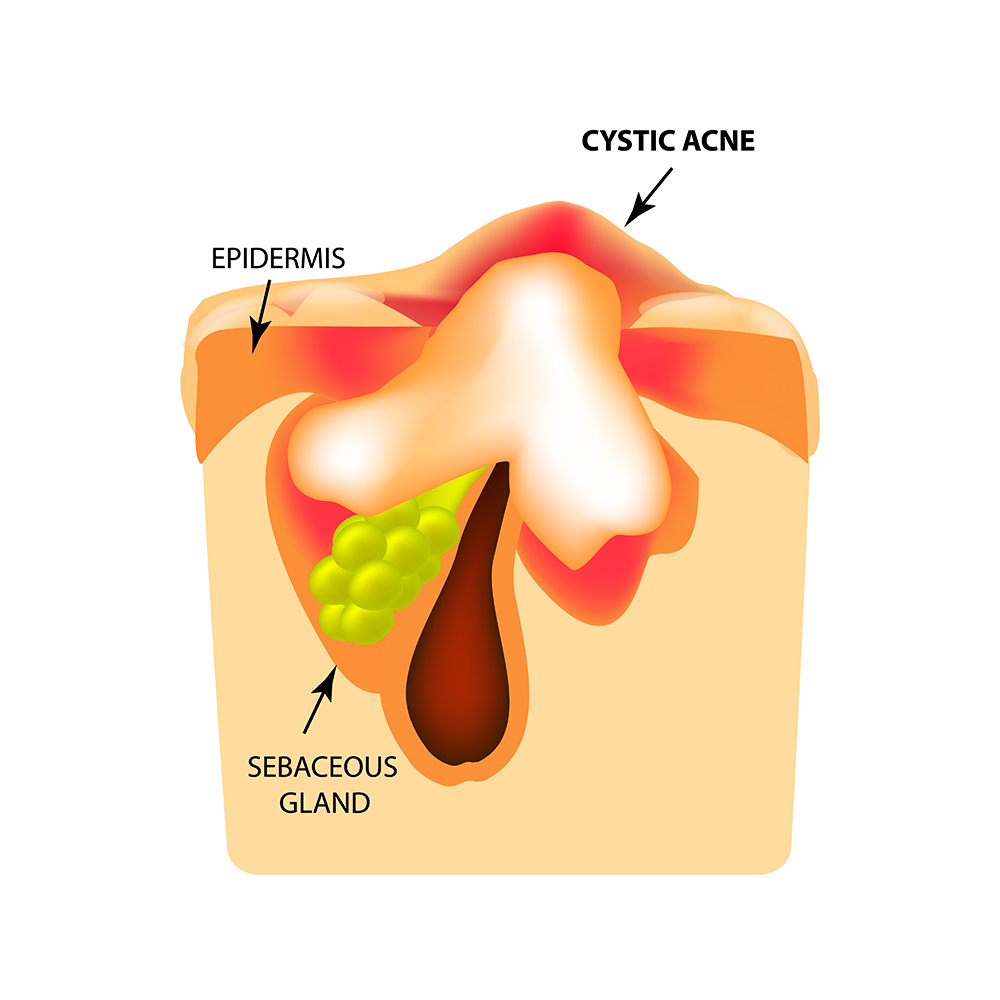
There are different types of inflammatory acne, according to the redness, size and pain level of the spot, and the potential of developing a scar.
Inflamed spots
Inflamed spots are red/pink bumps on the skin of variable size from a small pin head up to a few centimeters. These spots can be mildly inflamed, usually they are small and not too painful
Pustules
Pustules are formed when the pore is clogged by sebum, dead skin cells and P. acnes bacteria, which cause an inflammation that attracts white blood cells. Pus is simply a white blood cells accumulation that protect the body from infections. Pustules are small bumps on the skin that contain fluid or pus. They usually present as white bumps surrounded by red skin. These bumps look very similar to pimples, but they can become bigger than the usual spot. Pustules may develop on any part of the body, but they most commonly form on the back, chest, and face. They may be found in clusters in the same area of the body.
Cysts and nodules
Acne with cysts and nodules is characterized by large and painful spots that go deep within the skin layers. At first the clogged pore is filled with blood and later with pus, resulting in a large, hard to the touch, uncomfortable cyst. These spots can stay there for weeks or even months if not treated. Eventually, the deep spots harden and leave deep scars if miss traded.
Nodules are larger than regular pimples, because they form in a deeper level of the skin. These complicated and sore spots can become deep cysts and leave scars that are hard to cover.
Acne with cysts and nodules is the worst case of acne. The cysts are big, deep and filled with pus, they can reach up to a size of 2.5 cm or more. This kind of acne is usually genetic and is most common for teen boys and young men. The best treatment for this type of acne, and the chance of avoiding deep scaring, is to seek professional help from dermatologists and cosmeticians.
